Ace Maker DAO
Whitepaper
Ace Maker DAO is a decentralized finance platform (DeFi) that offers friendly services and apps for financial and economic activities, as well as venture investment in the multimedia industry. The platform is a DAO that runs on the Ace Maker protocol with open-source code, as part of the Ace Stream project. The goal of the platform is to provide secure and effective tools for decentralizing the multimedia market.
Definition of terms and brief explanations
The term "DAO" (Decentralized Autonomous Organization) refers to a complex form of smart contracts in which the rules of the decentralized organization are written into contract code and managed through tokens.
The term "decentralized multimedia market" refers to financial and economic activities related to the production of video and audio content, followed by its distribution and consumption in decentralized networks using peer-to-peer (P2P) data storage and streaming technologies (such as BitTorrent, Ace Stream, etc.)
About Ace Stream
Ace Stream is an international project aimed at building a decentralized media platform. It was developed actively in 2013 with support from the European Union.
Ace Stream is now the most popular decentralized multimedia platform for online streaming. It uses P2P (peer-to-peer) technology and has an environmentally friendly data storage and delivery system. This helps reduce CO2 emissions and protects the environment from damage caused by the centralized streaming industry and unicast technologies.
More than 30 million people use Ace Stream and it adds around 50,000 new users every day. People use it on their desktops, phones, TV boxes, and web browsers. This success has been achieved without any advertising or special incentives for users.
The Ace Maker DAO ecosystem is based on DLT (Distributed Ledger Technology) and does not have owners in the traditional sense; is owned by the community
The software operates in a decentralized, open network with a transparent economy based on embedded software algorithms presented in public smart contracts (open source codes) with complete decentralization of regulation of relationships, economic mechanisms, and settlements between its Participants. The rules of the Ace Maker DAO are maintained by the protocol (software code) itself, and all decisions regarding key system parameters are made by the social consensus of its Participants through voting.
The control rights of the Ace Maker DAO platform are distributed among the holders of AMD tokens. They manage the Ace Maker protocol and financial risks, ensuring stability, transparency, and efficiency of the protocol's operation. For this purpose, a scientifically-based management system is in place, which includes surveys and administrative voting.
All 100% of the AMD tokens are initially locked in the protocol. The primary placement (sale) on the market is carried out directly by the protocol itself (through smart contracts, with programmed pricing algorithms), and all funds generated from sales are automatically deposited into the Ace Maker DAO treasury and are fully controlled by the participants of the Ace Maker DAO (AMD holders).
Price Calculator
Ace Maker DAO is introducing innovative technologies and financial tools to the media and crypto markets, offering unique solutions not found anywhere else.
The Ace Maker DAO platform leverages the exclusive features of Ace Stream to reach a vast audience of millions of users, providing a one-of-a-kind proposition for content creators and distributors that is irresistible. Content producers are offered the opportunity to unlock liquidity and significantly increase their capitalization through the tokenization of unused and unrecognized assets; monetize their content in decentralized P2P networks and receive large advance payments from the outset; eliminate the problem of piracy with the use of Ace Stream technology; and other unique opportunities, all without cannibalizing existing sources of income.
The Ace Maker protocol provides a mechanism for forming a self-governing investment pool, in the form of a DAO, for decentralized venture investment in the multimedia market, with a predicted minimum income level.
The ability to predict a minimum level of passive income from funds invested in the protocol is one of the key aspects that adds value to the Ace Maker protocol and to the AMD tokens.
Profit Calculator
To provide clarity, we will present the calculations for predicting the minimum level of profitability of the AMD token, based on the basic parameters of the protocol, taking into account only one of the sources of passive income forming the protocol's reward pool.
Holders of AMD tokens receive a privileged opportunity to become co-owners of broadcasting rights from leading global producers of premium content (sporting organizations, film studios, music labels, etc.) at the most favorable terms in the world and will receive passive income from the full cycle of content production, broadcasting and distribution, without the need for direct participation in any of these processes.
The presence of an automated content distribution system, enabled by the protocol, gives Ace Maker DAO another unique feature and added value
The Ace Maker protocol offers not only user-friendly services and apps that provide mechanisms for secure investing and income forecasting, but also loyalty mechanisms that allow AMD holders to exit the DAO with minimal costs. Withdrawing funds from the protocol in one year incurs a 1.5% commission fee, in two years - 0% fee. This loyalty program is only available to the participants who buy AMD tokens in rounds 1 to 100.
The Ace Maker protocol aims to minimize risk by reducing the possibility of losses to almost zero.
AMD tokens are expected to become a flagship product in the De-Fi market. This is because they are the first crypto asset to offer decentralized venture investment opportunities in the multimedia market, with minimal risk and a guaranteed minimum return that is ensured by the Ace Maker protocol (platform software code)
Along with DeFi programs, the Ace Maker protocol will provide the market with a new decentralized stable digital currency, with a soft peg to currencies of different countries (called Ace Coin). This currency will be backed by trustworthy and highly liquid digital assets, including the most valuable assets of the internet, such as broadcast and content access rights (premium content), unlimited CDN bandwidth with prepaid traffic (guaranteed internet bandwidth for delivering content to consumers), and advertising inventory in the most efficient formats.
The foundation of Ace Coin's stability lies in its connection to the most valuable assets of the Internet, which make up the backbone of the Internet and its consumer value (content consumption, content delivery, and monetization). These assets are protected from seizure and central regulation. This is what sets Ace Coin apart and should be the basis for any stable digital currency in a decentralized and independent Internet.
Ace Coin serves as a stable form of currency, preserving its value. It can be used just like traditional money, but with the added benefits of convenience and efficiency.
The Ace Coin, besides its standard features and capabilities, can also serve as a means of unlocking liquidity, generating investments, and boosting capitalization. Financial institutions and providers of goods and services can independently issue the required amount of Ace Coins, offering guarantees for their return to the protocol, to obtain low-cost investment resources without the need for creating and marketing their own tokens and stablecoins in the market. The Ace Maker protocol features flexible and reliable collateral mechanisms, offering favorable lending terms for Ace Coins with a fixed interest rate ranging from 0.5% to 3% per year, depending on the collateral and the borrower's creditworthiness. Additionally, the issuer is given the chance to multiply the Ace Coins they create and receive through the "Premium Asset" program. Through the Ace Maker protocol and the emission of Ace Coins, individuals can generate low-cost investments and grow their capital with minimal risk and without using their own funds.
For example
A bank can create the necessary amount of Ace Coins for itself, tied to the currency of its choice, by placing its digital bond or digital certificate in a collateralized storage facility (as a guarantee of its obligation to return the Ace Coins taken in debt to the protocol in a timely manner). In this way, the bank gains access to these stablecoins at an annual interest rate of 0.5% to 3% (depending on its rating) and can sell them through its own or authorized institution (with the appropriate license), thereby attracting cheap fiat money from the entire global internet community, not limited to its current territorial area of operation. Furthermore, the bank can allocate a portion of the stablecoins it creates to an investment pool within the protocol (through AMD), thereby having the opportunity to multiply its Ace Coins with the help of the "Premium Asset" program, and the ability to withdraw its invested stablecoins through a return mechanism, with a commission of only 1.5%
In such a model, the only "risk" for the bank is solely in terms of the amount of earnings - how much it will earn (more or less)!
Empower your finance with Ace Maker DAO: Take control, ensure stability, and drive efficiency!
Primary objectives¶
The primary objectives of the Ace Maker DAO are:
- To create a DeFi protocol that builds an ecosystem for effective decentralized financial and economic activity in the multimedia market and to improve the Internet as a whole.
- To protect the interests of copyright holders and legalize content in peer-to-peer networks, which is an integral component of the capitalization of the decentralized multimedia market and the operation of the Ace Maker protocol.
- To tokenize broadcasting rights and access to content with the automation of content distribution processes and placement of such crypto assets on the market.
- To form a self-regulated investment pool and create exclusive DeFi programs for decentralized venture investment in the multimedia market with minimal risk and a predictable minimum return.
- To implement a multi-currency mechanism for creating decentralized stable digital currencies, backed by highly liquid crypto assets and the most in-demand digital goods and services, with a soft peg to currencies of different countries.
DeFi Protocol for Multimedia Market¶
Our mission is to create a DeFi platform with efficient mechanisms and reliable tools for building a decentralized media market ecosystem, where the interests of all participants (investors, content creators, content distributors and consumers, software and hardware solution providers, etc.) are taken into account and protected.
By directing the development of the media market towards maximum decentralization, we aim to not only improve the media market, but also the entire Internet, making it the way it was originally intended and the way it should be in the end!
With the goal of establishing a decentralized financial and economic system in the multimedia market, the Ace Stream project has undergone restructuring, made necessary updates, and delegated part of its functionality to the Ace Maker protocol and its community (DAO).
The Ace Maker and Ace Stream tandem transforms the Network into a decentralized ecosystem for the production, broadcasting, and consumption of multimedia content. This ecosystem takes into account the interests of all its participants, including their requests and preferences, as well as social aspects and technical features of decentralized, open-source technologies.
Ace Maker and Ace Stream: Revolutionizing Multimedia¶
Ace Maker and Ace Stream are transforming the rules of the multimedia market.
By delegating a portion of its technological functionality to the Ace Maker protocol and its community (Ace Maker DAO, token holders of AMD), Ace Stream introduces a multitude of features that extend far beyond multimedia streaming. The most significant innovation is the integration of P2P streaming with P2P finance (also known as DLT - Distributed Ledger Technology).
Both P2P video/audio streaming and DLT are not new, but combining them together can fundamentally change the market. This combination opens up a multitude of possibilities, and here are just some of the capabilities being realized in the Ace Maker + Ace Stream tandem:
- The tokenization of broadcast rights and content access, which has a market volume measured in billions of dollars per year.
This means that tokens issued by Rightsholders (hereinafter referred to as "Rightsholder Tokens") will be backed by enforceable agreements where the rights and obligations of the parties are executed by smart contracts. As a result, rightsholders will be able to attract additional investments and significantly increase their capitalization, while the crypto market will be able to receive new high liquidity crypto assets worth billions of dollars into circulation.
-
The registration, transparent accounting, and tracking of media market assets through DLT.
-
Ace Stream technology offers new and unique opportunities for token issuers and their holders:
- Unlimited bandwidth, with access to the "last mile" and the ability to broadcast to an unlimited number of simultaneous viewers anywhere in the world (unlike centralized technologies such as Unicast). This is complemented by the ability to broadcast with the best audio-visual content quality, several times higher than the quality of centralized services, while delivery costs are almost 10 times lower compared to centralized CDNs.
- The ability to organize access to content based on any tariff plans (subscription for a period of time; one-time access; per-minute billing) without the need to register users on the content provider's portal.
- LTS (Legal Torrent Stream) - a system for legalizing and monetizing content in one-level (P2P, peer-to-peer) networks. This is a unique (unmatched in the world) and effective solution for combating "pirate" content in decentralized networks that provides 100% protection of the interests of rightsholders when content is uncontrolledly distributed through P2P technologies.
-
"Carbon Negative" Effect with the Use of P2P Broadcasting Technologies
The "Carbon Negative" effect is achieved by reducing the load from international trunks/data centers/CDN and redistributing it among the consumers’ devices that do not bear any additional energy load. As a result, when someone consumes content through Ace Stream or other P2P broadcasting technologies instead of alternative content consumption through centralized services and Unicast technologies, the amount of CO2 emissions into the atmosphere is reduced. If P2P technology is not used, the content consumption will occur in any case and in equal volumes, but only through Unicast technologies, with the corresponding CO2 emissions.
One hour of video viewing in the Ace Stream decentralized network using P2P technology instead of alternative video viewing through centralized online services and Unicast technologies, on average, reduces the amount of carbon emissions into the atmosphere by 131 g, which is equivalent to the average monthly level of decarbonization of one coniferous and deciduous tree (86 g and 143 g of carbon sequestration, respectively) that has been grown for 10 years.
More details here
-
Exclusive DeFi programs for reliable and predictable venture investment in the multimedia market.
The integration of protocols and smart contracts has laid the foundation for creating a business logic under which participants in the DeFi program Ace Maker protocol can become co-owners of broadcasting rights from leading global premium content producers (sporting organizations, movie studios, music labels, etc.), predict the protocol's profit and receive income from the full content production, broadcasting, and distribution cycle without the need for direct participation in any of these processes. On a programmatic level, conditions will be recorded and all obligations will be met with full assurance of mutual settlements between parties.
-
Tracking of traffic and time, which cannot be falsified, allows for precise automated mutual settlements between all participants.
- Low entry threshold for investing in the multimedia market due to decentralization and automation.
About the Ace Maker Protocol¶
The Ace Maker Protocol is a decentralized financial application built on the Ethereum blockchain.
Finance and economics are the foundation of stability and reliability in any system, especially in a decentralized one. That's why we didn't reinvent the wheel in such an important and responsible aspect, to avoid putting the Participants of the platform at risk, but rather use tried and tested technologies that have been proven over time and by millions of users.
The Ace Maker Protocol is built on the foundation of the Maker DAO protocol, one of the most reliable and advanced specialized platforms in the decentralized finance space. To ensure stability and reliability in our decentralized system, we have opted to leverage the tried and tested technology of Maker DAO, rather than reinventing the wheel. Our protocol incorporates the fundamental elements of Maker, while also adding new features and tools that are specifically tailored to the multimedia market through integration with the decentralized multimedia technology of Ace Stream. In essence, the Ace Maker Protocol offers all of the capabilities of the parent (base) protocol, but with additional enhancements and opportunities that are directly aligned with the multimedia market.
Ace Maker protocol offers the multimedia market with the necessary mechanisms and tools to carry out effective financial and economic activities in decentralized networks. In addition, Ace Maker protocol will play an equally important role in the cryptocurrency market. By integrating with the Ace Stream protocol, Ace Maker enables the creation and release of highly liquid tokenized assets backed by the most valuable and in-demand resources of the internet, such as:
- Broadcasting rights and access to premium content (TV channels, sports events, movies, series, music);
- Advertising inventory in the most sought-after formats;
- Unlimited P2P CDN bandwidth with prepaid traffic to ensure delivery of content to end-users anywhere in the world with maximum audio-visual quality and stability of broadcasts.
Protection of the Interests of Right Holders¶
Introduction¶
The decentralized media market, characterized by millions of users consuming multimedia content through P2P technologies with traffic volumes reaching as high as 25% of total international Internet traffic in some regions and trending upward, is a rapidly growing industry. However, despite its large audience and abundant high-quality content, it lacks financial economics and, as a result, remains un-monetized. This issue stems from two main factors:
- The absence of a solution that effectively protects the interests of content owners in this market segment
- The lack of mechanisms and financial instruments that would enable the effective monetization of content when published and distributed in decentralized P2P networks.
Streaming P2P Video in Current Realities¶
In the existing reality, P2P streaming video has become a significant part of the multimedia industry.
Peer-to-Peer (P2P) video streaming technologies are gaining increasing attention from broadcasters due to their undeniable advantages over traditional centralized (server and/or CDN) technologies. However, the absence of mechanisms to protect the interests of rights holders and the inability to monetize content using decentralized broadcasting technologies forces rights holders to rely on centralized CDN solutions. The provision of modern formats (4K) and quality content delivery to a large number of users leads to massive capital expenditures (servers, CDN, dedicated data centers, etc.) and operational expenses (ensuring broadband capacity, energy consumption, and a large number of personnel), which ultimately causes significant harm to the environment and the Internet as a whole and results in high prices for end-users. This, in turn, leads to high demand for "pirated" content. Eco-friendly and convenient P2P solutions, which provide the same or better user experience, are usually much cheaper, although they are completely devoid of centralized management capabilities. This combination of features makes P2P networks particularly attractive to "pirates," which effectively creates another massive problem in the form of the widespread distribution of unlicensed content in decentralized networks, resulting in huge harm to the entire multimedia industry.
Relevance of the Problem of “Piracy”¶
The combined losses incurred by content owners due to illegal production and distribution of content have reached $2.3 trillion in 2022, according to the Frontier Economics analytical agency.
According to data from the U.S. Chamber of Commerce’s Global Innovation Policy Center, piracy of digital video reduces the overall revenue of the industry by 11% to 24%. The study estimates that "online piracy" costs the economy of just one country, such as the United States, a minimum of $29.2 billion in lost profits each year. And these are the most conservative estimates!
The Continued Relevance of Content Piracy: An Analysis of Consumer Behavior
On the day of the premier of the first episode of the 8th season of the popular television show "Game of Thrones," a reported 3.39 million individuals in the United Kingdom viewed it on Sky Atlantic, while 17.4 million residents in the United States viewed the episode on HBO within the first 24 hours of its release. However, these figures are overshadowed by the number of individuals who utilized unauthorized streams and torrents to view the episode. Digital piracy agency MUSO recorded 54 million illegal views of the first episode of the 8th season within the first 24 hours of its release.
These data demonstrate that consumers continue to turn to unauthorized sources in search of content, despite significant global efforts to combat piracy in recent years, and once again highlights the inefficacy of current standard methods for combating the dissemination of unlicensed content.
The Achilles' heel of the sports industry¶
The issue of "piracy" is relatively new to the sports industry, as sports leagues were previously not significantly impacted by this problem due to the unique characteristics of the industry. Many in the sports industry still believe that everything is fine, but the truth is that the growth of revenue from the sale of sports rights, which was once considered to be endless, has come to an end, leaving the industry completely unprepared to face the realities and address the major challenges posed by the new decentralized technologies and the growing spread of unlicensed sports transmissions.
The problem is worth over 36 billion dollars per year!
The global market for the rights to broadcast sporting events is estimated to be approximately $50 billion annually, according to foreign research agencies. Meanwhile, more than half of sports fans (51%) watch at least one "pirated" (unlicensed) sports broadcast per month, according to research company Ampere Analysis. A survey conducted by Synamedia revealed that among those who watch illegal sports broadcasts, 42% consume sports content on a daily basis.
The study was conducted in 10 countries and
involved around 6,000 sports fans, according to Broadband TV News
It can be confidently assumed that the level of unauthorized viewing reduces the overall revenue of the industry by 42% to 51%, leading to the sports industry missing out on over 36.2 billion dollars in yearly revenue, plus the cumulative profits of all licensed sports broadcasters.
The issue of piracy is particularly dangerous for the sports industry, as once major broadcasters (buyers of sports broadcast rights) fully understand the extent of unauthorized sports broadcasts, they may begin to view all rights to sports as non-exclusive, leading to a significant decrease in current revenue from the sale of licensed broadcast rights. This is already happening.
The CEO of beIN Media Group, Youssef Al-Obaidly, emphasized the urgency of the "piracy" problem during an industry summit and stated that the "glorious media rights bubble" is about to burst, predicting that the economic model of the industry will be completely rewritten.
At present, there is no satisfactory solution to this problem. Efforts to take legal action against pirates using P2P distribution channels (such as BitTorrent) face numerous technical and legal difficulties and have limited potential for success. BitTorrent clients (as well as Ace Stream clients) are merely the means of transport and cannot control what their users download or view. Traffic filtering not only undermines the principle of network neutrality and borders on censorship, but is also extremely costly and can easily be bypassed by even moderately tech-savvy internet users. This clearly demonstrates that the policy of legal and technological restrictions is no longer effective in the changing technological context, and anyone who wants to see their assets protected must seek more adequate solutions.
Changes in the Media Landscape¶
The majority of rightsholders, particularly sports leagues and broadcast rights owners, are troubled by the proliferation and widespread distribution of unlicensed transmissions in P2P (peer-to-peer) networks, such as Sop Cast and Ace Stream. While these technologies are themselves lawful and legitimate, they also happen to be accessible and effective broadcast technologies, providing anyone with the opportunity to use them for any purpose, including unlicensed broadcasting. In the case of Ace Stream, it is also a fully decentralized technology, with no means of blocking any broadcast, unlike the partially decentralized SopCast and centralized services.
For a long time, rightsholders have repeatedly approached Ace Stream to find an effective solution to the active widespread distribution of unlicensed content through the use of decentralized technologies like Ace Stream.
Ace Stream envisions its future as a universal decentralized multimedia delivery network, providing legal content and considering the interests of all participants in such a network. Therefore, resolving the cluster of issues described above is imperative.
Commercialization instead of censorship¶
Ace Stream's approach to protecting the interests of rightsholders involves providing new mechanisms and financial tools that enable rightsholders to monetize their assets in a more flexible manner, aligned with contemporary content distribution channels. In this way, piracy can be defeated economically, rather than by force!
Legal Torrent Stream (LTS) - system of legalization and monetization in Peer to Peer networks.
The LTS system, at the software level, ensures that the rights holder is paid for each minute of playback of their content when using Ace Stream technology, regardless of who is distributing the content and through which websites, services, or applications, and on which devices the playback will be carried out.
Technological guarantees
Ace Network has unique feature of fully decentralized and transparent traffic and watching time accounting system and payment system based on most advanced blockchain technology.
Rightsholders will get paid automatically and will be provided with tools for Network monitoring and audit to be absolutely confident about reliability of statistics of watched minutes and correctness of payments.
The network's node code is open source.
To incentivize rightsholders to utilize LTS and actively participate in the proposed decentralized ecosystem, the mechanisms of the Ace Maker protocol provide the opportunity for rightsholders to receive an advance payment, equal to 10% of their total revenue from the sale of broadcasting rights for the previous yearly period.
For example, if the total yearly revenue of the English Premier League (EPL) from the sale of TV rights and centralized streaming services was 5 billion dollars, then utilizing the Ace Maker offer, this organization could receive an advance payment from the decentralized market in the amount of 500 million dollars, as additional income without cannibalizing their other sources of revenue.
Why LTS is a genuine instrument in elimination of pirated content in P2P networks and whether Ace Stream will be effective?
Genuineness and efficiency of the Ace Stream solution is that it is fully decentralized and automated, and its program algorithms rely on compromise which considers interests of all parties, including bad actors (“pirates”), and all parties get unique features and opportunities.
Opportunities for copyright holders¶
- Maximum audience reach and monetization of content in decentralized P2P networks with an automated distribution system, providing access to a new and previously untapped market segment with a multi-million audience, capable of generating additional revenue streams without affecting other sources of income.
-
Solving the issue of widespread distribution of unlicensed content in decentralized networks, where it is not possible to block it through legal or technological means.
Guaranteed payment to the rightsholder for each minute of content reproduction in the Ace Stream network.
-
Unlocking liquidity and increasing capitalization by creating new highly liquid crypto assets (issuing proprietary digital assets backed by rights to broadcast and access to content in decentralized P2P networks), attracting investment capital from the crypto market through token sales on auctions and exchanges, as well as direct sales.
-
Broadcasting to an unlimited number of simultaneous viewers, in the best quality, to any location worldwide.
No technical limits for the amount of simultaneous viewers online (in contrary to common technologies like unicast). It is complemented by the best audio visual quality of broadcasts and minimal expenses on content delivery (up to 10 times cheaper than with Unicast) for independent broadcasting of own content.
-
Control of advertisement views related to copyrighted content in the Ace Stream Network.
- Partnership programs with Network members for better monetization of content (Live Bets, In-Play Bets, Marketplaces etc.).
- Positive impact on the environment through the use of eco-friendly P2P CDN.
- Improved image through interaction with advanced internet users, who are largely adopters of decentralized technologies.
Opportunities for "Pirates"¶
- Broadcasters and website/app owners who publish and distribute copyrighted content without proper licensing are given the chance to legitimize their services, earn revenue from legal distribution, and increase their profits without incurring additional costs, bureaucracy, or direct interaction with rightsholders.
Advantages for Users¶
- Users will continue to enjoy services and applications with the functionality they are accustomed to, which is not available in centralized services, as well as additional features, such as:
- Access to all necessary TV channels, sports events, movies, TV shows, music, without registration
- Convenient search and cataloging, with the ability to play content anywhere and any way, without being limited to a specific site, application, player, and device
- The highest possible "true" audio-visual quality of content, several times higher than the quality of centralized services
- Flexible approach to tariff plans and premium content packaging, with business models that they can afford
- Receiving bonuses and rewards: for providing their hardware and network resources; for publishing and distributing content; for watching advertisements; for moderating content and actively participating in the life and development of the Network.
DAO Governance Tokens¶
Owners of rights, as well as platform developers and any internet users, have the opportunity to engage in the development of policies and protocols of Ace Stream and Ace Maker through the use of DAO governance tokens.
One-of-a-kind offer that's too good to pass up¶
The synergy of Ace Stream and Ace Maker creates a no-brainer offer on a software level, benefiting all platform participants and network users.
Ace Maker's unique proposition for rightsholders lies in the fact that today, only the Ace Stream network and Ace Maker protocols possess all the necessary components to effectively protect the interests of rightsholders in decentralized P2P networks.
Without protection mechanisms for rightsholders in the world's most popular decentralized online broadcasting network (Ace Stream), which is rapidly growing and globally used by various broadcasters, and the lack of legal and technological means to remove unauthorized content from the network, the problem of widespread unauthorized content cannot be solved.
Ace Maker invites rightsholders to thoroughly explore the capabilities offered by the protocol and carefully evaluate its prospects for use or rejection, to make a simple and obvious choice.
A Simple and Obvious Choice for Rights Holders
What rights holders need to consider to make an informed decision?
Today's technology landscape already allows for not only decentralized P2P broadcasting, but also the formation of a fully decentralized economy with the highest level of privacy and anonymity, as well as the ability to build fully decentralized services and funding mechanisms that cannot be blocked or hindered in any way. This means that all current standard methods of combating the distribution of unlicensed content (such as removing content from websites upon request by rights holders, blocking websites entirely, limiting the operation of "pirate" services with financial institutions, identifying the organizers of unlicensed broadcasting and the physical location of their servers for the purpose of bringing legal action and confiscating the equipment of copyright infringers, etc.) will soon stop working altogether and will no longer yield any positive results.
As a result, rights holders are faced with a simple and obvious choice, consisting of only two options:
- Utilize the proposed decentralized mechanisms (protocols and smart contracts) to effectively solve the "piracy" problem, enter a new market, and reap the benefits of a wide range of new opportunities that will provide substantial profit for rights holders, or
- Decline the offered opportunities and passively observe the widespread distribution of their content in decentralized P2P networks, which will continue to grow and cannot be stopped by any legal or technical means, thus continuing to feed the mills of the "pirates."
Andy Chatterley, CEO of MUSO
It is important copyright holders understand the pirate audience is one of their most loyal fans who mainly presents a huge commercial opportunity
Tokenization of broadcast and access rights¶
Tokenization is a method of issuing a new financial instrument to attract investments, using secure DLT technology, allowing to attract a global Internet audience to purchase such assets and secure high consumer confidence.
The Ace Maker protocol provides a mechanism for tokenizing rights to broadcast content and access rights to content by issuing two types of tokens:
- Copyright holder tokens - tokens backed by the rights to broadcast, providing access to the issuer's content, both created and to be created in the future.
- Content provider tokens - tokens backed by the rights of access to the services and offerings of content providers.
The responsibility for linking content with the copyright holder falls on the Oracle
Oracle is a bridge between the offline world and the decentralized system. In a real world Oracle is a company that can make legal decisions and execute actions based on these decisions in the blockchain. Oracles can be added or removed from the blockchain by vote of network owners.
Tokens issued by content producers and content providers represent materialized agreements where rights and obligations are executed through smart contracts. These tokens essentially become specialized currencies created to pay for specific goods or services. To access protected content and services provided by content providers, one must first purchase these "specialized currencies" (tokens). This purchasing process can be fully automated and seamless for users, while also being convenient for content providers.
The rights provided by these tokens are valid indefinitely and only cease to exist upon their utilization (when the services are received and the token is utilized).
Token issuance can be done through various user interfaces, including the basic system portal Eden and various interfaces developed by the community.
Copyright Holder Token¶
Copyright holder tokens are only created by the content producer and will be used in the future to access premium, copyright-protected content.
This type of token can only be used to access premium (paid) content that is not freely available. For example, if the token issuer places some of their content on YouTube or somewhere else that is freely accessible, this token will not be used to pay for access to that content (network users and oracles are responsible for enforcing these conditions).
In other words, Ace Stream network users will automatically receive the rights to access such content for free (without using tokens), while the copyright holder will have the right and opportunity to activate the advertising monetization model for such content, subject to payment for traffic.
These tokens are in compliance with the ERC20 standard. Each token contains:
- One hour of access to the issuer's content
- Classifier: AVoD (Audio and Video on Demand) or Live (Live Streams)
- Tokenized amount of one hour's worth of data transmission in the Ace Stream P2P CDN (1 AceTime, which is automatically generated at the time of token issuance)
The issuance of this kind of tokens should be carried out by rights holders for the following purposes:
- To tokenize the rights to broadcast their premium content, which has already been created and will be created in the future, with the aim of unlocking liquidity and increasing their capitalization, by obtaining additional sources of revenue funding through the creation of new highly liquid crypto assets and attracting investment capital from the crypto market.
- To provide the rights to broadcast to third parties, on the conditions of payment for access to their content through tokens issued by them.
- To use the LTS mechanism, which ensures the protection of the rights holders' interests in the Network.
- To monetize content in a decentralized P2P network with the involvement of per-minute billing.
This type of token has additional backing in the form of pre-purchased, tokenized bandwidth in a P2P CDN network, which is acquired by the Ace Maker protocol at a discounted rate. This ensures that token holders have a reliable P2P CDN system and the ability to deliver high-quality content to end-users with minimal CDN costs.
In other words, up to 95% of the costs typically incurred by content providers for content delivery to end-users are embedded in the structure of these tokens and covered by the Ace Maker protocol. This provides content providers with the most favorable conditions in the world, both in terms of acquiring rights to content and delivering it to end-users.
To issue this type of token, the rights holder signs a contract with the Oracle and submits a token issuance request through any convenient network portal. Optionally, issuers may receive an advance payment at the time of token creation, equal to 10% of the issuance volume. This amount is calculated based on the nominal token price and paid from the DAO treasury funds, subject to approval by the DAO participants via voting.
The system's fee for token issuance and management is 30% of the issued token volume (set by system settings and subject to change by DAO voting).
Application Submission¶
A token issuance application is submitted by the rights holder or agent and contains the following information:
- Address of the electronic version of the contract in the IPFS network
- Token name
- Token classifier:
- AVoD (audio and video on demand)
- Live (live broadcasts)
- Traffic classifier:
- multimedia (video + audio)
- audio
- Token nominal price (expressed in stablecoins)
- Currency to which the token being issued will be linked (USD, EUR, or others supported by the system)
- Issuance volume (the value of tokens issued should not exceed three times the total revenue from the sale of broadcast rights for the previous fiscal year, based on the nominal price of the token. The optimal value is equal to the annual value)
- Volume of tokens for primary sale, guaranteed for buyout (the issuer indicates the percentage of tokens from the total issuance that must be immediately bought out by the protocol at the nominal price, at the time of their issuance)
- Application validity period
- Oracle account address (responsible for confirming copyright and signing the off-chain contract)
- Agent account address (deal organizer responsible for ensuring the rights and interests of the issuer within the system)
Application parameters:
ipfsContractAddress: the IPFS network address of the electronic version of the contracttokenName: the name of the issued tokentokenClass: the token classifier (live or AVoD)trafficClass: the traffic classifier (multimedia or audio)tokenBasicValue: the nominal price of the token expressed in stablecoinstokenCurrency: the currency of the tokentokenAmount: the amount of tokens to be issuedpresaleShare: the amount of tokens for the initial sale at nominal value (in percent)maxDuration: the duration of the applicationoracleAccount: the address of the oracle accountagentAccount: the address of the agent account
After submitting the application, it must be approved by authorized participants in the following order:
- The Oracle (specified in the application)
- Ace Stream DAO representative (authorized account)
- Ace Maker DAO, if a primary sale has been declared.
If there is no primary sale (presaleShare is set to zero), approval from Ace Maker DAO is not required.
If the application is not approved within the specified maxDuration, it will automatically be cancelled.
Token Issuance¶
The issuance of copyright holder tokens is performed using the issueTokens method of the TokenizedCopyrightsManager smart contract. This method is automatically triggered upon approval of the application by the system participants (as per the aforementioned procedure).
If a presale volume was specified in the request, then at the time of issuance, Ace Maker DAO automatically purchases the specified volume of tokens at the nominal price using funds from the Ace Maker DAO treasury. The issued tokens are placed in the basic asset storage, which is automatically created during issuance.
If there is no presale in the application, then the issued tokens are not classified as a basic asset of the protocol and after issuance, they are placed in a special system storage designated for storing tokens that have been passed on to the protocol to be sold.
Also at the time of issuance, the smart contract uses the "AceByte" tokens to create the "AceTime" tokens, which are encapsulated in the copyright holder tokens in an amount that corresponds to the volume of rights generated for access to the issuer's content. The necessary volume of AceByte tokens is determined by the Ace Stream smart contracts responsible for the automatic issuance of time tokens.
In order to reduce the cost of content delivery, "AceByte" tokens are initially purchased from the Ace Stream DAO in the amount of 1 billion tokens with a 75% discount.
Token definitions:
- AceByte (XAB) - native token of the Ace Stream network, backed by guaranteed P2P CDN bandwidth and used for traffic accounting purposes with a ratio of 1 AceByte = 100 GB of traffic. AceBytes are necessary for creating AceTime tokens, based on one hour of content playback, taking into account the average traffic consumption in the Ace Stream Network.
-
AceTime (XAT) - algorithmic token, backed by the amount of consumed traffic, in a ratio of one hour of video and/or audio content playback. AceTime tokens can be used to pay for one hour of content delivery in the Ace Stream P2P CDN, regardless of the amount of GB used.
The Ace Time token is technically represented by a set of multiple tokens, each of which is tied to a specific type of content:
- Ace Time Multimedia - a token that can be used to pay for the delivery of one hour of multimedia content (audio + video)
- Ace Time Audio - a token that can be used to pay for the delivery of one hour of audio content
To create one AceTime token, a certain number of AceByte tokens are required, calculated as follows:
aceTimePrice = trafficRate / 100where:
aceTimePrice- the number of AceByte tokens needed to create one AceTime tokentrafficRate- the average level of traffic consumption for the corresponding type (multimedia, audio) in the Ace Stream network (GB/hour)
Circulation of rights holder tokens¶
Once issued, all tokens go into the appropriate vault and serve for intra-system operations, such as: pricing and confirming the volume of rights; distributing revenue to the owners of the copyright holder tokens, in the form of deductions when paying for access to content. At the same time, the owners of tokens can dispose of the rights to those tokens in a seamless and most convenient way, through NFT.
Each token holder is issued an OwnerNFT - a non-exchangeable token (NFT) representing the rights to own a certain share of the issuer's tokens. Owners have the ability to transfer their share (in whole or in part) to another owner (by transferring/selling OwnerNFT)
The Contract Algorithm¶
- The issuance of
tokenAmounttokens takes place. - Using the smart contract
AceTimeManager(Ace Stream DAO), the amountaceByteAmountof AceByte tokens required to createtokenAmountAceTime tokens is calculated. aceByteAmountof AceByte tokens is transferred to theAceTimeManagercontract.- The
AceTimeManagercontract createstokenAmountAceTime tokens. These tokens are encapsulated in the issued copyright holder tokens. trafficTokenPriceis calculated - the cost of one AceTime token in stablecoins based onaceByteAmountand the price at which the Ace Maker DAO purchased the AceByte tokens.- If a primary sale is specified in the request (
presaleAmount > 0):- Payment for the purchase of primary sale tokens (in stablecoins) is transferred from the Ace Maker DAO treasury to the issuer's account:
presaleAmount = tokenAmount * presaleShare% * tokenBasicValue
- A new vault is created for basic assets with a specified liquidity ratio (this parameter is passed when the request is finally confirmed by a DAO vote).
- The issued tokens are placed in the created vault.
- As a result of the asset being deposited in vault, stablecoin emission takes place in the amount of:
aceCoinIssueAmount = tokenAmount * tokenBasicValue / liquidityRatio
- Payment for the purchase of primary sale tokens (in stablecoins) is transferred from the Ace Maker DAO treasury to the issuer's account:
- The issued stablecoins are transferred to the Ace Maker DAO treasury.
- If there is no primary sale, the issued tokens are placed in a special system storage designated for storing tokens passed to the protocol to be sold.
- The token owners are assigned:
- Ace Maker DAO - in the amount of the system fee plus
presaleShare(the primary sale volume), minus oracle and agent's reward and contributions to charity, development and marketing - Agent - a percentage of the system fee is paid to the agent (system setting)
- Ace Maker DAO Charity Treasury - 10% of the system fee minus oracle and agent reward
- Ace Maker DAO Development Treasury - 5% of the system fee minus oracle and agent reward
- Ace Maker DAO Marketing Treasury - 5% of the system fee minus oracle and agent reward
- Issuer - the rest of the emission volume
- Ace Maker DAO - in the amount of the system fee plus
- An OwnerNFT is generated for each owner.
- The values of
tokenBasicValue,tokenCurrency,trafficTokenPrice,tokenClassandtrafficClassare recorded on the blockchain (used in later algorithms to pay for access to content).
Token Issuance Example
For this example, we'll use the following input data:
- Token name: CHT
- Token classifier: live (live broadcasts)
- Traffic classifier: multimedia (multimedia traffic)
- Token issuance volume: 1000 CHT (corresponds to 1000 hours of viewing)
- Current level of multimedia traffic consumption in the Ace Stream network: 4 GB/hour
- Price at which Ace Maker DAO purchased AceByte tokens: 0.25 USD
- Token currency: USD
- Nominal token price: 0.04 USD
- Liquidity ratio: 1.5
- Initial sale volume: 10%
- Application validity period: 3 months
- System fee: 30%
- Oracle and agent reward: 10% of the system fee
- Charity contributions: 10% of the system fee minus oracle and agent reward
- For development: 5% of the system fee minus oracle and agent reward
- For marketing: 5% of the system fee minus oracle and agent reward
After the application is submitted, authorized participants have 3 months to sign it, otherwise the application will be canceled.
The application includes an initial sale, so final confirmation is done by voting of Ace Maker DAO and the emitted tokens are placed in the base asset storage with the specified liquidity ratio (1.5). The issuance of tokens is executed at the time of application confirmation, in the same transaction. This is done by calling the issueTokens method of the TokenizedCopyrightsManager smart contract, which performs the following actions:
- A storage for base assets with a liquidity ratio of 1.5 is created
- 1000 CHT are emitted and placed in the created storage
- 26.67 USD stablecoins (1000 * 0.04 / 1.5) are emitted and transferred to the Ace Maker DAO treasury
- The emitted tokens will encapsulate AceTimeMultimedia tokens because the traffic classifier is “multimedia”
- The number of AceByte tokens needed to create AceTimeMultimedia tokens is calculated:
- formula:
aceTimePrice = trafficRateMultimedia / 100 aceTimePrice = 4 / 100 = 0.04(this is the number of AceByte tokens needed to create one AceTimeMultimedia token)- To create 1000 AceTimeMultimedia tokens, 1000 * 0.04 = 40 AceByte tokens are needed
- 40 AceByte tokens are transferred to the AceTimeManager contract. 1000 AceTimeMultimedia tokens are created and encapsulated in the emitted tokens
- formula:
- trafficTokenPrice, the cost of one AceTimeMultimedia token in stablecoins, is calculated:
- formula:
trafficTokenPrice = aceTimePrice * aceBytePurchasePrice, where:trafficTokenPrice- cost of one AceTimeMultimedia token in stablecoinsaceTimePrice- number of AceByte tokens needed to create one AceTimeMultimedia tokenaceBytePurchasePrice- price at which Ace Maker DAO purchased AceByte tokens
- calculation:
trafficTokenPrice = 0.04 * 0.25 = 0.01 stablecoins
- formula:
- 4 stablecoins are transferred from the Ace Maker DAO treasury to the emitter's account (this is payment for the initial sale: 1000 * 0.04 * 10% = 4)
-
Token owners are assigned:
- 60% - emitter
- 31.6% - Ace Maker DAO (30% system fee, plus 10% of the volume of the initial sale, minus 3% oracle and agent rewards, minus charity, development and marketing contributions)
- 3% - oracle and agent rewards (10% of the system fee)
- 2.7% - Ace Maker DAO Charity Treasury
- 1.35% - Ace Maker DAO Development Treasury
- 1.35% - Ace Maker DAO Marketing Treasury
-
An OwnerNFT is generated for each owner, confirming their right to hold CHT tokens.
Pricing¶
To determine the real value of tokenized assets for right holders, pricing is carried out in several stages, forming three pricing positions:
Nominal Price¶
The nominal price is the minimum price set taking into account the possible transaction.
When tokens are issued, the issuer and authorized oracles of the Ace Stream and Ace Maker networks establish the minimum price at which the tokens are offered to the first owners when they are initially placed.
Fair Price¶
The fair price is the price reflecting all future income or utility that the token can bring to the right holder. It is formed through the conduct of open auctions, involving professional participants of the multimedia market.
To form the fair price of the copyright holder tokens, an auction is held. A portion of the OwnerNFTs received by the system in the form of fees is put up for auction. The volume of OwnerNFTs put up for auction is 5% to 10% of the total issuance of the copyright holder tokens and can be changed by a DAO vote.
The auction takes place in two stages:
- First stage: English auction
- OwnerNFTs are put up for sale in fixed lots at a price equal to the sum of the nominal price (
tokenBasicValue) and the price of the AceTime token (trafficTokenPrice). - The first participant must offer a price not lower than the initial price of the lot.
- Each subsequent participant must offer a higher price than the previous participant.
- If the next bid is not exceeded within a certain time, the second stage starts.
- If there were no bids at the auction within a certain time, the auction is restarted.
- OwnerNFTs are put up for sale in fixed lots at a price equal to the sum of the nominal price (
- Second stage: Dutch auction
- A lot from the first stage is put up for sale at an inflated price (130% of the maximum bid of the first stage).
- Every 90 seconds, the lot price decreases by 1%.
- The participant can buy the whole or part of the lot at the current price at any time.
- The auction ends when the entire lot is sold.
- The auction is restarted if the lot was not sold within a certain period of time, or if the lot price fell below a certain value.
- All auction parameters are set by system settings.
Market Price¶
The market price is the price of access to content that is formed on the market in accordance with demand and supply.
After the auctions, the copyright holder tokens are placed on exchanges at the formed fair price to determine the exchange rate, which is affected by yield, reliability, and many other factors.
This exchange rate (market price) is received by the protocol from the oracles in real-time and determines the price limit, which sets the minimum token price (corresponding to the cost for 1 hour of video playback), guaranteed for payment to the right holder at the software level (protocol, smart contract). In the event that any broadcaster sets a price below this price limit, the price will be automatically adjusted by the oracle to the minimum limit level. This limit is set in the smart contract and is guaranteed by the protocol.
Automated Management and Distribution¶
The automation of management and distribution processes for the purpose of providing passive income to OwnerNFT holders is unique and an added value of this token. The functionality of the Ace Stream protocol and Ace Maker smart contracts has allowed the implementation of a business logic in which the owners of this type of token can earn income not only from speculative operations but also from the entire content production, broadcasting and distribution cycle without the need for direct participation in any of these processes. At the software level, the conditions will be recorded and all obligations of the parties will be fulfilled with full guarantees of mutual settlements.
Holders of OwnerNFTs (owners of copyright holder tokens stored in the system storage) receive a portion of the income from the payment for access to content, in accordance with the conditions of the ContentAccessPayment smart contract.
ContentAccessPayment is a system smart contract that is responsible for processing payments received as payment for access to content.
Contract Description¶
This contract is triggered upon a user's payment for access to content. The cost of access is dynamically calculated and includes the following components:
- Cost of copyright holder tokens (calculated based on hours of viewing and a fair token price)
- OwnerNFT holders fee (expressed as a percentage, system setting)
- Broadcaster fee (in stablecoins, set by the broadcaster)
- Distributor fee (in stablecoins, set by the distributor)
- System transaction fee (in stablecoins, system setting)
The funds received from the user are distributed according to the components listed above:
- OwnerNFT holders receive:
- the amount equal to the fair cost of copyright holder tokens, minus the cost of encapsulated AceTime tokens
- a fee in the form of a percentage of the fair cost
- The broadcaster and distributor receive their respective fees
- The system transaction fee
The portion of the OwnerNFT holders is distributed proportionally based on their ownership ratios of the issuer tokens in the Ace Maker protocol.
This contract burns the issuer tokens used for access to their content. The AceTime tokens, which were contained within the issuer token for payment of content delivery, are released and transferred to the RewardUploadersManager contract for distribution among viewers through a "lottery" system.
The "Lottery" System¶
The Lottery System is an automatic reward system that incentivizes viewers to use P2P technologies by financially rewarding them for providing the Network with their hardware and network resources.
This system performs a raffle of rewards among users who actively participated in seeding content (providing traffic to other users).
Algorithm
The smart contract RewardUploadersManager is responsible for the implementation of the Lottery System.
- To participate in the raffle, users must have contributed at least 1 GB of traffic.
- For every 1 GB of traffic provided, the participant receives 1 lot.
- The raffle is held every 28 days, triggered by calling the
rewardmethod, which randomly selects winning lots and transfers the reward to them. - The maximum number of lots per user is calculated using the formula:
maxLots = accessPrice / trafficPrice, where:accessPriceis the cost of access to content (in stablecoins)trafficPriceis the cost of 1 GB of traffic in stablecoins (currently 0.01$ per 1 GB)
- The winning coefficient is 1:100:
- every 100th lot is a winning one
- the winning lot receives a reward equivalent to the cost of 100 GB of traffic
The winning coefficient can be changed by a vote of the Ace Maker DAO.
The Lottery System provides a fair and transparent way of distributing rewards among users who contribute to the network's traffic, motivating them to continue to participate actively in the network
Contract Algorithm¶
Parameters
sourceAccount: the user (viewer) account that pays for access to the content.issuerAccount: the account of the copyright holder tokens issuer.broadcasterAccount: the account of the broadcaster.distributorAccount: the account of the distributor.accessAmount: the consumption volume (number of hours of viewing).
Algorithm
- Find the issuer's token contract
chTokenusingissuerAccountas reference - If
sourceAccountholdschTokentokens:tokenCostis set to 0- Burn
accessAmountof issuer's tokens fromsourceAccount
-
If sourceAccount does not hold
chTokentokens:- Request the current fair price of
chTokentoken (chTokenFairPrice) from the system -
Calculate the cost of issuer's tokens:
tokenCost = accessAmount * chTokenFairPrice -
Deduct the cost of encapsulated AceTime tokens:
trafficCost = accessAmount * chToken.trafficTokenPrice tokenCost = tokenCost - trafficCost -
Calculate the fee for OwnerNFT holders:
tokenMarginCost = tokenCost * SystemSettings.content_access_owner_nft_margin -
Burn accessAmount of issuer's tokens from the system storage
- Deduct
tokenCost + tokenMarginCoststablecoins fromsourceAccountand distribute among OwnerNFT holders - Burn
trafficCoststablecoins
- Request the current fair price of
-
Calculate the broadcaster's fee:
broadcasterFee = accessAmount * broadcasterAccount.fee -
Calculate the distributor's fee:
distributorFee = accessAmount * distributorAccount.fee -
Transfer all the AceTime tokens contained in the issuer's tokens to the
RewardUploadersManagercontract for distribution among viewers through the "lottery" system. -
Transfer
broadcasterFeestablecoins from sourceAccount to broadcasterAccount -
Transfer
distributorFeestablecoins from sourceAccount to distributorAccount -
Deduct
SystemSettings.network_feestablecoins (fixed transaction fee of the system) from sourceAccount.
Examples¶
Example 1 (user does not have copyright holder tokens)
For the example, let's use the following inputs:
- consumption volume: 100 hours of viewing
- copyright holder token name: CHT
- copyright holder token contract address: chtContract
- user does not have CHT tokens
- current fair price of the token: 1 CHT = 0.05 stablecoins
- price of encapsulated AceTime token: 0.01 stablecoin
- OwnerNFT holders' fee: 10%
- OwnerNFT holders list:
- 25% - Ace Maker DAO
- 15% - ownerA
- 60% - ownerB
- system fee: 0.02 stablecoin
- broadcaster fee: 0.01 stablecoin per hour
- distributor fee: 0.015 stablecoin per hour
As a result of the ContentAccessPayment smart contract execution, the following actions are performed:
- 100 CHT are burned from the system storage
- 100 AceTime tokens (contained within 100 CHT) are transferred to RewardUploadersManager contract for distribution among viewers through a "lottery" system
- cost of the burned CHT is calculated: 5 stablecoins (100 CHT were burned, fair price of each is 0.05 stablecoin)
- cost of encapsulated AceTime tokens: 1 stablecoin (100 * 0.01)
- OwnerNFT holders' fee: 0.4 ((5 - 1) * 10%)
- broadcaster fee: 1 stablecoin (100 hours * 0.01)
- distributor fee: 1.5 stablecoins (100 hours * 0.015)
- 7.9 stablecoins are deducted from the user (5 + 0.4 + 1 + 1.5) and distributed as follows:
- 4.4 is distributed among OwnerNFT holders (fair cost minus AceTime token cost plus fee 10%):
- 1.1 is transferred to the Ace Maker DAO treasury (25%)
- 0.66 is transferred to ownerA's account (15%)
- 2.64 is transferred to ownerB's account (60%)
- 1 is transferred to the broadcaster
- 1.5 is transferred to the distributor
- 1 is burned (cost of encapsulated AceTime tokens)
- 4.4 is distributed among OwnerNFT holders (fair cost minus AceTime token cost plus fee 10%):
- 0.02 is deducted from the user (system transaction fee)
Example 2 (user has copyright holder tokens)
In this example, the inputs are the same as in the previous example, with the exception of:
- user has 100 CHT on their account
Result of the smart contract execution:
- 100 CHT are burned from the user's account
- 100 AceTime tokens (contained within 100 CHT) are transferred to RewardUploadersManager contract for distribution among viewers through a "lottery" system
- broadcaster fee: 1 stablecoin (100 hours * 0.01)
- distributor fee: 1.5 stablecoins (100 hours * 0.015)
- 2.5 stablecoins are deducted from the user (1 + 1.5) and distributed as follows:
- 1 is transferred to the broadcaster
- 1.5 is transferred to the distributor
- 0.02 stablecoin is deducted from the user (system transaction fee)
Content Provider Token¶
Content Provider Tokens are created by content providers and will be used in the future to access their services and products, as either a subscription or a one-time purchase. These tokens are non-fungible (NFT) and conform to the ERC-721 standard.
Content providers should issue these tokens for the following purposes:
- To tokenize the access and payment mechanism for their services and products, with options for subscriptions or one-time access (with time restrictions)
-
To create personalized pools with the "Premium Pool" service function
The "Premium Pool" service allows any broadcaster (content provider or OTT service) to create pools with a common subscription or equal access conditions to their services, thus eliminating the need for users to register and purchase subscriptions for each individual OTT service. This eliminates the problem of "subscription fatigue" and makes the service more convenient and attractive for both premium content creators and consumers.
In brief, the problem of "subscription fatigue" is that too many streaming services (about 300 only in the US) lead to growing consumer disappointment due to the need for multiple subscriptions and services. 43% of those surveyed by Deloitte last year admitted to "giving up" the search for content, and 48% said it was difficult to find what they wanted to watch on different services.
Similarly, a study conducted in October 2019 by TV Time and United Talent Agency (UTA) showed that 70% of respondents believe that there will soon be too many streaming services. 87% said that services are becoming too expensive. Respondents also expressed disappointment with the need to switch between different services (67%), difficulties setting up and managing accounts (58%), and the inability to easily find content (45%).
The amount paid by the user for a subscription to a personalized pool is proportionally distributed by the Distribute Subscriptions smart contract among its participants (content providers), based on the percentage of total time spent by the subscriber playing the content of one or another pool participant (for which the calculation is made), compared to the total time spent by the subscriber playing the content of other pool participants. Details of the distribution algorithm can be found in the smart contract description (a fully open and transparent system without any possibility of manual control or interference in its operation).
-
To aggregate external content within the service
This type of token allows the content provider to legally add to their service content from any copyright owners, other content providers, and broadcasters participating in the Network. This is made possible through the use of the Ace Stream and Ace Maker smart contract technologies, which provide a necessary legal framework, reliable protection for all Network participants, and effective distribution mechanisms for maximum benefit for all parties.
-
Ace Stream P2P CDN Utilization
The use of Ace Stream P2P CDN enhances the audio-visual quality and stability of transmissions in existing services while reducing content delivery costs by a factor of 10 compared to traditional centralized technologies. This allows for broadcasting to an unlimited number of simultaneous viewers anywhere in the world without technical limitations.
Optimizing Financial Flows for Issuers
This type of token does not encapsulate AceTime tokens and all P2P CDN traffic settlements are made based on actual consumption. The token features a demand-based issuance and activation mechanism to avoid double spending on the Ethereum network.
The system fee for token issuance is 15% of the total volume of tokens emitted and can be changed by a DAO vote. Fee payments are made in stablecoins at the time of token sale, when the user pays the content provider for the purchased token.
Token Issuance¶
The issuance of tokens of this type is carried out by the ContentAccessManager smart contract. The content provider can independently (without the involvement of any authorized system participants) carry out the issuance of this type of token through any convenient network portal, by paying a one-time registration fee.
Registration of Issuance¶
Registration is performed through the registerAccessToken method of the ContentAccessManager contract:
- Any network account can be the issuer.
- The issuer must register in the network.
- The issuer pays a one-time registration fee (a small fixed amount set by system settings).
- After registering in the network, the issuer can issue an unlimited number of tokens as needed.
- The issuer pays a transaction fee in the Ethereum network.
Registration Parameters¶
accessDuration: The duration of the access (in seconds)contentList: A reference to the document with a list of content identifiers that access is granted toprice: The price of the token in stablecoins
Token Circulation¶
The ContentAccessManager smart contract enables unlimited automatic issuance of any token registered in the system using the following algorithm:
- A user calls the
ContentAccessManagercontract to purchase a token. - The payment for the token is deducted from the user and distributed as follows:
- A portion is received by the Ace Maker DAO (system fee)
- The remainder is reserved for settlement (refer to the “Settlements” section)
- The contract emits the token and transfers it to the user.
- The user pays a transaction fee in the Ethereum network.
To gain access to the issuer's service, the token must be activated. A user of the issuer's service who holds a token can activate the token directly on the issuer's portal (on the website, in the app, etc.) or through any other convenient portal in the network
Settlements¶
Content provider's users can access the services of other system’s participants. In this scenario, payment for these services is based on usage and facilitated by the token issuer, which is the content provider. The settlements that can occur include:
- Payment for P2P CDN traffic usage
- Provision of copyright holder tokens for access to their content
- Payment for broadcaster services
In the event that the content provider's account lacks sufficient funds, the corresponding service will automatically be disconnected and become unavailable to the content provider's users.
For the benefit of content providers, a system for reserving funds for settlements has been implemented. This system streamlines the settlement process and reduces the risk of service interruption. It operates as follows:
- Funds received from the user during token issuance are reserved for settlements
- As the user consumes services, the reserved stablecoins are used to pay for these services if necessary
- Unused funds from the reserve are unlocked in equal portions every 28 days starting from the moment the token is activated, until the token's validity period expires (refer to the "Unlocking the Reserve" example).
IMPORTANT: The reserve system cannot guarantee that the content provider has sufficient funds for settlements, therefore it is recommended that content providers closely monitor their balance.
It is important to note that the content provider acts as a distributor for the system and will receive a distributor's fee where applicable.
Contracts Algorithms¶
Token Registration¶
Registration is performed using the registerAccessToken method, which:
- Records the token parameters (
accessDuration,contentList,price) in the blockchain - Withdraws payment for registration (a fixed number of stablecoins, system setting) from the issuer
- The issuer pays the transaction fee in the Ethereum network
Token Issuance¶
Issuance is performed using the issueAccessToken method. This method is called by the issuer's service user who wants to purchase a token:
- The token price in stablecoins is withdrawn from the user
- The received stablecoins are distributed:
- A portion goes to Ace Maker DAO, in the amount of the system fee
- The remainder is reserved for settlements (see “Settlements” section)
- A new instance of the token is emitted and transferred to the user
- The user pays the transaction fee in the Ethereum network
The user can activate the token immediately during issuance by passing the autoActivate=1 parameter to the issueAccessToken method. This will save on Ethereum network fees by not launching a separate transaction for token activation.
Token Activation¶
Activation is performed using the activateAccessToken method. This method is called by the current token owner:
- The token status changes to
active - The activation date and time are recorded in the token
- The token owner pays the transaction fee in the Ethereum network
Examples¶
Registration
The following system configurations are used in the example:
- Registration fee - 100 stablecoins
- System fee - 15%
Alice (the content provider) wants to issue access tokens for her service. To do this, Alice visits the network portal and fills out the token registration form with the following fields:
- Access duration - 28 days
- Price - $5
- Link to the content list - Alice uploads a link to her service playlist here.
Next, Alice clicks the "Register" button, signs the transaction in her crypto wallet, and pays the transaction fee on the Ethereum network.
After the transaction is confirmed, the ContentAccessManager smart contract performs the following actions:
- Alice is charged 100 stablecoins (emission fee)
- Alice's token is added to the list of tokens registered in the system.
Now Alice can sell her tokens using the tools provided by the community (portals, SDKs).
Token Purchase and Activation
Bob (the user) wants to purchase access to Alice's service. To do this, he visits Alice's portal or any of the community portals and buys a token there:
- He clicks the "Buy" button on the portal
- He signs the transaction in his crypto-wallet
- He pays the transaction fee in the Ethereum network
- The cost of one token, 5 stablecoins, is deducted from Bob's account and distributed as follows:
- 0.75 stablecoins are deposited into the Ace Maker DAO treasury (15% system fee)
- 4.25 stablecoins are reserved for settlement (see the settlement example below)
- A new token instance is issued and transferred to Bob's account
Bob can activate the token either at the time of purchase or later, on Alice's portal or on one of the community portals, or in applications that support the Ace Maker protocol. An activated token gives Bob the right to use Alice's service for 28 days starting from the activation date.
Settlements
When conducting settlements, funds reserved at the time of token purchase are used. In this case, it is 4.25 stablecoins.
Let's consider several examples of settlements depending on whether Alice is a broadcaster and whether Bob viewed the content requiring the copyright holder tokens.
Example 1
In this example, Alice is not only a distributor but also a broadcaster, and also has rights to all the content she provided Bob with access to. In other words, copyright holder tokens are not required to access the content. Alice only has to pay for the traffic. If Alice has AceByte tokens in her account - they will be used to pay for the traffic. If not - they will be purchased using funds from the reserve.
Input:
- Access cost: 5 stablecoins
- Access duration: 28 days
- Over the 28 days, Bob watched content for 50 hours and used 150 GB of traffic
- 1.5 AceByte is required to pay for the traffic (since 1 AceByte = 100 GB)
- The current market price of one AceByte token: 1 USD
Settlements:
- Bob is charged 5 stablecoins (access cost)
- 0.75 stablecoin is transferred to the Ace Maker DAO treasury (15% system fee)
- 4.25 stablecoins are reserved for settlements
- 0.02 stablecoin is paid from the reserve for system transaction fee
- If Alice has AceByte tokens:
- 1.5 AceByte is charged from Alice's account and transferred to the smart contract for distribution through the "lottery" system
- The remaining reserve (4.23 stablecoins) is unlocked and transferred to Alice's account
- If Alice does not have AceByte tokens:
- Automatic purchase of AceByte is performed in the required volume:
- 1.5 AceByte is purchased through the AceByteManager smart contract (Ace Stream DAO) at a cost of 1.5 stablecoin
- 1.5 AceByte is transferred to the smart contract for distribution through the "lottery" system
- The remaining reserve (2.73 stablecoins) is unlocked and transferred to Alice's account
- Automatic purchase of AceByte is performed in the required volume:
Example 2
In this example:
- Alice is both a distributor and a broadcaster
- Dave is the rights holder who issued tokens with broadcasting rights:
- Token name - CHT
- Current fair price - 1 CHT = 0.05 stablecoin
- Cost of encapsulated AceTime token - 0.01 (current price, including protocol discount)
- OwnerNFT holders fee - 10%
- Access cost: 5 stablecoins
- Access duration: 28 days
- Bob watched 50 hours of content belonging to Dave during the 28 days of using Alice's service (i.e. 50 CHT is required for access)
- OwnerNFT holders:
- 30% - Ace Maker DAO
- 70% - Dave
In this example, Alice must provide 50 CHT for access to the content. AceTime tokens, encapsulated in the rights holder tokens, are used to pay for the traffic. If Alice has CHT in her account, they will be used. If not, they will be purchased using funds from the reserve.
Settlements:
- 5 stablecoins are charged from Bob (access cost)
- 0.75 stablecoin are transferred to Ace Maker DAO treasury (15% system fee)
- 4.25 stablecoins are reserved for settlements
- 0.02 stablecoin are paid from the reserve (system transaction fee)
- If Alice has CHT tokens:
- 50 CHT are burned from Alice's account
- The remaining reserve (4.23 stablecoins) is unlocked and transferred to Alice's account
- If Alice does not have CHT tokens:
- The fair cost of 50 CHT (50 * 0.05 = 2.5 stablecoins) is paid from the reserve
- The cost of encapsulated AceTime tokens (50 * 0.01 = 0.5 stablecoins) is deducted from the fair cost. These 0.5 stablecoins are burned.
- A fee of 10% (0.2 stablecoins) is added to the remaining amount (2 stablecoins). The fees are paid from the reserve. A total of 2.2 stablecoins are distributed among OwnerNFT holders:
- 0.66 stablecoin (30%) - Ace Maker DAO
- 1.54 stablecoin (70%) - Dave
- 50 CHT are burned from the system storage
- The remaining reserve (1.53 stablecoins) is unlocked and transferred to Alice's account
- 50 AceTime tokens contained in CHT tokens are transferred to a smart contract for distribution through a "lottery" system.
Example 3
In this example, the inputs are the same as in the previous one, with the exception of:
- Alice is not a broadcaster - she is only a distributor
- The broadcaster is Fred
- Fred set his fee for access to the content - 0.01 stablecoin per hour
Alice must pay the broadcaster's fee to Fred and provide 50 CHT.
Settlements:
- Bob is charged 5 stablecoins (access fee)
- 0.75 stablecoin is transferred to the Ace Maker DAO Treasury (15% system fee)
- 4.25 stablecoin is reserved for settlements
- the system transaction fee of 0.02 stablecoin is paid from the reserve
- the broadcaster's fee is 0.5 stablecoin (50 hours * 0.01)
- 0.5 stablecoin is transferred from the reserve to Fred (broadcaster fee)
- if Alice has CHT tokens:
- 50 CHT are burned from Alice's account
- the remaining reserve (3.73 stablecoin) is unlocked and transferred to Alice's account
- if Alice does not have CHT tokens:
- the fair cost of 50 CHT (50 * 0.05 = 2.5 stablecoin) is paid from the reserve
- the cost of the encapsulated AceTime tokens (50 * 0.01 = 0.5 stablecoin) is subtracted from the fair cost. These 0.5 stablecoin are burned.
- A fee of 10% (0.2 stablecoins) is added to the remaining amount (2 stablecoins). The fees are paid from the reserve. A total of 2.2 stablecoins are distributed among OwnerNFT holders:
- 0.66 stablecoin (30%) - Ace Maker DAO
- 1.54 stablecoin (70%) - Dave
- 50 CHT are burned from the system storage
- the remaining reserve (1.03 stablecoin) is unlocked and transferred to Alice's account
- 50 AceTime tokens, which were contained in the CHT tokens, are transferred to a smart contract for distribution through a "lottery" system.
Example of Reserve Unlocking
This example describes the algorithm for unlocking funds from the reserve when the token validity period exceeds 28 days.
Let's assume Bob purchased a token from Alice for 364 days (1 year) and 13 stablecoins were reserved for settlements.
The unlocking will be carried out in equal parts every 28 days starting from the moment the token was activated. This means that every 28 days, one stablecoin (13/364 * 28) will be unlocked, minus any funds that were expended from the reserve during these 28 days
Consider the following table as an example:
| # | Days passed from the activation | Amount to unlock | Spent in this period | Credited to Alice | Alice’s debt |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 28 | 1 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0 |
| 2 | 56 | 1 | 0.2 | 0.8 | 0 |
| 3 | 84 | 1 | 1.5 | 0 | 0.5 |
| 4 | 112 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 1.5 |
| 5 | 140 | 1 | 0.5 | 0 | 1 |
| 6 | 168 | 1 | 0.5 | 0 | 0.5 |
| 7 | 196 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0.5 |
| 8 | 224 | 1 | 0.5 | 0 | 0 |
| 9 | 252 | 1 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0 |
| 10 | 280 | 1 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0 |
| 11 | 308 | 1 | 0.3 | 0.7 | 0 |
| 12 | 336 | 1 | 0.3 | 0.7 | 0 |
| 13 | 364 | 1 | 0.2 | 0.8 | 0 |
| Total | 13 | 8.5 | 4.5 |
Note: If the token is valid for 28 days or less, the reserve will be unlocked once at the end of the token's validity period.
AMD Token in the Ace Maker Protocol¶
The primary objective of the Ace Maker protocol is to provide a decentralized mechanism through DAO (Decentralized Autonomous Organization) to create a self-governed investment pool with exclusive DeFi programs for venture investing in the multimedia market with minimal risk and predictable minimum returns. The key component of this mechanism is the AMD token.
The AMD token is an ERC20 standard token designed to manage the Ace Maker protocol and assets of the Ace Maker DAO. The token's base value is determined by the rewards pool, and holders can stack their tokens to receive rewards generated by the Ace Maker protocol from various protocol income sources.
Holders of AMD form a self-governed investment pool and organize the operation of the Ace Maker protocol. They control the Ace Maker protocol and financial risks by making decisions on all key parameters (conditions, fees, types, and size of collateral, etc.) through voting among AMD token holders.
The number of votes is proportional to the number of AMD tokens that the participant sends to the voting contract address, DSChief. One AMD token sent to the voting contract address equals one vote. In other words, the more AMD tokens a voting participant contributes, the greater influence they have on the final decision.
Use of the AMD Token in Ace Maker Governance¶
Owners of AMD tokens (management tokens of the Ace Maker protocol) have the right to vote on changes to the Ace Maker protocol. All participants, not just AMD token owners, can propose ideas for voting.
Approved protocol changes from voting do not usually take effect immediately. If the voters activate the Governance Security Module (GSM), implementation of the decision can be delayed for up to 24 hours and blocked by a veto. The technical committee, selected through voting and consisting of special system participants, has the right to veto the voting results. Any AMD holder can be elected to the technical committee.
This delay and veto process gives AMD token holders the ability to protect the system in case of malicious governance proposals, either by blocking the decision with the technical committee or by launching an emergency shutdown mechanism. An example of such a proposal could be an idea to change the security parameters in violation of established monetary policy or to allow the disabling of protection mechanisms.
AMD holder voting can elect accounts with temporary veto rights. These accounts have the right to veto the results of any vote, but their veto power is limited by time. The list of limitations is determined by a smart contract that is ratified by voting. An example of such a contract could be a time limit (for example, one year) or until a certain event in the system occurs (depending on which occurs first).
Polling and Executive Voting¶
In practice, the Ace Maker Governance process includes proposal polling and Executive Voting. Proposal polling is conducted to establish a rough consensus of community sentiment before any Executive Votes are cast. This helps to ensure that governance decisions are considered throughtfully and reached by consensus prior to the voting process itself. Executive Voting is held to approve (or not) changes to the state of the system.
At a technical level, smart contracts manage each type of vote. A Proposal Contract is a smart contract with one or more valid governance actions programmed into it. It can only be executed once. When executed, it immediately applies its changes to the internal governance variables of the Ace Maker Protocol. After execution, the Proposal Contract cannot be reused.
Any Ethereum Address can deploy valid Proposal Contracts. AMD token holders can then cast approval votes for the proposal that they want to elect as the Active Proposal. The Ethereum address that has the highest number of approval votes is elected as the Active Proposal. The Active Proposal is empowered to gain administrative access to the internal governance variables of the Ace Maker Protocol, and then modify them. If the Governance Security Module (GSM) is activated, the launch of the active proposal is delayed for 24 hours. During this period, the technical committee has the right to veto and cancel the proposal launch. To veto, ⅔ of the technical committee members must support the decision by voting in the internal committee vote (in which each committee member has one vote).
AMD Holder Rights and Responsibilities¶
AMD holders can vote to:
- Approve a list of content producers and terms for creating public offerings for rights holders;
- Approve or reject a content producer's request for token emission with an initial sale;
- Approve the type of assets and conditions for their acquisition to automate the redemption process through the Ace Maker DAO Treasury;
- Form programs for utilizing Treasury funds (DeFi programs, investment and reinvestment, infrastructure financing, etc.);
- Add a new type of collateral with its own risk parameters;
- Add new risk parameters or modify existing ones for one or more approved types of collateral;
- Change the interest rate for loans and savings;
- Select oracles that verify copyright or infringement;
- Select oracles that provide price feeds;
- Select technical committee members with veto power over any vote to protect the system;
- Change auction settings within the system;
- trigger Emergency Shutdown;
- Update the system;
AMD token holders can also allocate funds from the Ace Maker DAO Treasury to pay for various infrastructure projects and services, including building infrastructure for agents and oracles, market research and risk management programs. The Ace Maker DAO Treasury is funded from the sale of AMD tokens and system fees collected by the protocol from the issuance of copyright holders tokens, as well as from lending programs, stability fees, liquidation fees, and other sources of income.
Issuance and Distribution of AMD Tokens¶
The initial issuance volume is 10 billion AMD.
The nominal price (initial token price of AMD at the start of sales): 1 AMD = $1.
All of the initial AMD issuance is blocked by smart contracts and distributed as follows:
- 30% - to the Ace Stream project
- 7% - for development programs (rewards for network participants who provide legal and consulting support, technological development, and marketing programs for Ace Maker DAO). Participants (recipients) can be any legal or physical entity approved by the DAO vote
- 3% - to advisors and agents (rewards for individuals who advise DAO members and execute trades on their behalf)
- 60% - open protocol offer (direct sales and auctions automatically carried out by the protocol through smart contracts)
Initially, all 10 billion AMD are blocked in the SaleAMD smart contract (this contract regulates the sale of AMD). The unblocking of AMD is performed by the SaleAMD contract using the following algorithm:
- as a result of the purchase of
NAMD tokens,Ntokens are unblocked and transferred to the buyer's account N/2tokens are unblocked and transferred to the Ace Stream DAO treasuryN/20tokens are transferred to the advisor and agentN * 7/60tokens are transferred to the Ace Maker DAO treasury for reward programs
Example
- the buyer purchased 60 AMD
- 7 AMD are unblocked and transferred to the Ace Maker DAO treasury for reward programs
- 3 AMD are unblocked and transferred to the accounts of the advisor and agent in the ratio specified by the buyer
- 30 AMD are unblocked and transferred to the Ace Stream project's treasury
The blocked tokens that are allocated to the Ace Stream project and reward programs can be used for voting in the Ace Maker DAO, but cannot be used for participation in revenue distribution or any other purposes (DeFi programs, etc.) until they are unblocked.
The funds received from the sale of tokens unblocked by the SaleAMD contract are automatically distributed as follows:
- 90% - for the acquisition of tokenized broadcasting rights (copyright holder tokens)
- 10% - for technological development and marketing programs of the Ace Maker DAO
AMD Sale¶
AMD tokens are sold exclusively by the SaleAMD smart contract. The exclusivity means that only this smart contract can sell and unlock AMD tokens, providing complete transparency in this process.
There are two mechanisms for the sale of AMD: auction and retail sale.
The auction is intended for the sale of large volumes of AMD. Lots with different amounts of AMD (for example, 100 thousand, 500 thousand, 1 million, etc.) are put up for auction. The size of the lots is set by system settings. The starting price at the auction is equal to the current nominal value of the AMD token, which increases as the number of sold (unlocked) tokens increases. The pace of price growth is determined by the algorithm embedded in the SaleAMD smart contract (see the "Pricing Algorithm" section).
The retail sale mechanism allows for quick purchase of any amount of AMD, however the token price is higher than at the auction. Details are in the "Retail Sale" section.
Auction¶
Registration¶
To participate in the auction, when an advisor and/or agent will be involved in the transaction, registration is required. In the case where the buyer does not attract an advisor or agent, registration is not necessary.
The registration process:
- The buyer visits the network portal and fills out the registration form:
- The address of the advisor's account in the Ethereum network
- The address of the agent's account in the Ethereum network (the person who will trade at the auction on behalf of the buyer)
- The maximum amount of stablecoins that the agent can spend on the auction
- The maximum price of 1 AMD that the agent can use in auction bids
After registration, the agent has the right to participate in auctions on behalf of the buyer within the established limits.
The buyer signs the transaction in their wallet and pays the transaction fee in the Ethereum network.
Advisors and Agents¶
Ace Maker DAO is dedicated to providing maximum protection for DAO members from any risks and errors, which is especially relevant in decentralized blockchains where it is not possible to undo transactions. To achieve this goal, the protocol has implemented a motivation system that incentivizes the involvement of third-party professionals active in the market. Ace Maker will reward advisors and agents who provide consultation and facilitate auction transactions for DAO members. The compensation is equal to 5% of the transaction amount and will be paid in AMD tokens from the protocol's special reserve fund (Ace Maker DAO treasury).
As a decentralized organization run by a technological protocol (software code), Ace Maker DAO does not have the ability to perform qualification checks on advisors or agents and can only register and keep track of them. As such, it is up to the DAO members to attract these parties and perform their own qualification checks. In return, the protocol guarantees compensation for these parties through its system, so take advantage of this opportunity to protect yourself to the fullest extent.
The terms of the rewards program for advisors and agents are determined through a vote by the DAO.
An advisor is a physical or legal entity with an authorized account who carries out personal consultations in order to inform the DAO member about the mechanisms of Ace Maker DAO and the protocol on which it operates. Advisers are not allowed to provide investment advisory services unless they are authorized in accordance with the laws of the country/jurisdiction where they carry out such activities.
To become an advisor in the system and receive compensation, you must register and make a contribution. The cost of registration for one year is 1000 stablecoins (USD).
In addition to providing advice, an advisor may also act as a agent or appoint one if the DAO member does not have their own personal agent.
An agent is an authorized account that represents the DAO member (the buyer of AMD tokens) and can place bids on auctions on their behalf. The agent's actions are programmatically limited by two parameters:
- The agent can only make bids within the buyer's specified maximum price
- The agent cannot exceed the established limit for all auctions combined
When placing bids on auctions, the agent signs transactions in their wallet and pays transaction fees on the Ethereum network.
Agents will only receive compensation if they were appointed by an advisor and an advisor indicated their account in the distribution of rewards. If there is no advisor involved in the deal and the buyer directly indicates the agent as the party (account) to receive compensation, the agent will also be eligible for compensation.
The compensation is locked in the system for a period of time which is given to the buyer as a "grace period" (buyback option), The compensation is given to the advisor and the agent unless the buyer withdraws funds from the protocol within the specified period (1-2 years, according to the current terms). In that case, the compensation is burned.
Mechanics of buying through an agent:
- The agent places a bid on the auction, signs the transaction in their wallet, and pays the transaction fee on the Ethereum network.
- If the bid is won:
- Stablecoins for payment of the deal are transferred from the buyer's account, which the agent represents, to the SalesAMD smart contract.
- The buyer receives AMD in the amount of the lot size.
- AMD is reserved for the advisor and/or agent in the amount of 5% of the lot size, in the ratio indicated by the buyer or their advisor (if the advisor is authorized to appoint an agent). These tokens are paid out after the "grace period" if the buyer does not make a return on this deal.
Trading Balance¶
To participate in auctions, each participant must first deposit their trading balance in the Ace Maker protocol. Only transaction fees on the Ethereum network are charged for deposits and withdrawals of the trading balance.
The AMD Selling Mechanism¶
The sale of AMD on the auction takes place in two stages. On the first stage, lots with a fixed amount of AMD and a fixed minimum price are put up for sale. Payments must be done in the stablecoin approved by the protocol. The size of the lot is set by system settings (can be changed by voting in the Ace Maker DAO). The system may have several auctions with different lot sizes at the same time. The minimum price is set by the price growth algorithm embedded in the SaleAMD smart contract. On the second stage of the auction, participants compete by offering to receive less AMD for a fixed price established in the first stage.
The first stage: a direct auction, with the goal of selling a fixed amount of AMD at the highest price possible:
- A lot (fixed amount of AMD) is put up for sale at the current minimum price (see the minimum price determination algorithm below)
- Participants make their bids in stablecoins
- The first participant must offer a price not lower than the minimum
- Each subsequent participant must offer a higher price than the previous participant
- If no one outbid the next bid within the established time, the auction moves on to the second stage
- If there were no bids on the auction within the established time, the auction restarts
The second stage: a reverse auction, with the goal of selling the minimum amount of AMD at the fixed price established in the first stage.
- A lot (AMD tokens) is put up for sale at the fixed price equal to the maximum bid from the first stage
- At the start of the second stage, the size of the lot is equal to the size of the lot in the first stage
- Each subsequent participant must offer to receive less AMD at the same price
- The winner of the auction transfers the stablecoins to the AceMaker storage and receives the AMD (at this point, the SaleAMD smart contract executes the unlocking of the AMD according to the logic described above)
The reverse auction allows participants with limited financial capabilities to be competitive. By offering to buy less AMD at a fixed price, participants are effectively offering a higher price for one AMD, but without spending more stablecoins.
Example
- Alice is a buyer
- Alice replenishes her trading balance with 1 million stablecoins and registers for participation in auctions:
- she designates Bob as her advisor and agent (in one person)
- she allows Bob to spend up to 1 million stablecoins on auctions
- she allows Bob to use a maximum bid of 1 AMD = 2 stablecoins
- Bob participates in an auction with a lot of 100,000 AMD and wins, making a maximum bid of 200,000 stablecoins for the lot (1 AMD = 2 stablecoins)
- 200,000 stablecoins are deducted from Alice's account:
- 180,000 (90%) are transferred to the Ace Maker DAO treasury to purchase copyright holders tokens
- 20,000 (10%) - to technological development and marketing programs of Ace Maker DAO
- The SaleAMD smart contract unlocks 167,000 AMD:
- Alice receives 100,000 AMD
- 5,000 AMD (system reward) are reserved for Bob, which he will receive in one year if Alice does not cancel the deal (i.e. does not initiate a buyback of her 100,000 AMD)
- 50,000 AMD are transferred to the Ace Stream DAO treasury
- 12,000 AMD are transferred to the Ace Maker DAO treasury for reward programs
Retail Sale¶
The retail sale mechanism allows any Ethereum network account to purchase any amount of AMD tokens for stablecoins. The most important component of this mechanism is the pricing algorithm, which depends on the amount of AMD being purchased and the average maximum price of AMD token in auctions:
- The average maximum price of AMD token is calculated based on the last 10 auctions with a minimum lot size equal to or greater than the amount of AMD being purchased in the retail sale.
- The price of AMD token in the retail sale is equal to 110% of the calculated average price.
IMPORTANT: If the average price cannot be calculated due to the fact that there has been no participant in the auction with the corresponding lot size, the purchase through retail trading is not possible.
Example
- 125,000 AMD is purchased through the retail sale mechanism.
- Auctions for selling AMD have been launched with the following lots:
- 100,000
- 250,000
- 500,000
- The auction with a lot size of 250,000 is selected (the minimum lot size that is greater than 125,000).
- This auction has been closed 3 times with the following maximum prices of AMD token:
- 4 stablecoins for 1 AMD
- 5 stablecoins for 1 AMD
- 6 stablecoins for 1 AMD
- The average maximum price of AMD token: 5 stablecoins
- The price for the retail sale: 5.5 stablecoins (5 + 10%)
In the retail sale, there are no advisors and agents. Their rewards are transferred to the Ace Maker DAO treasury account for the "bounty" programs.
AMD Pricing Model¶
The minimum price of an AMD token on an auction is controlled by an algorithm embedded in the SaleAMD smart contract and cannot be changed.
Pricing Algorithm
Starting price: $1
The price increases after the sale of each 1 million tokens according to the formula:
Price growth chart for the sale of 6 billion from the initial issuance:
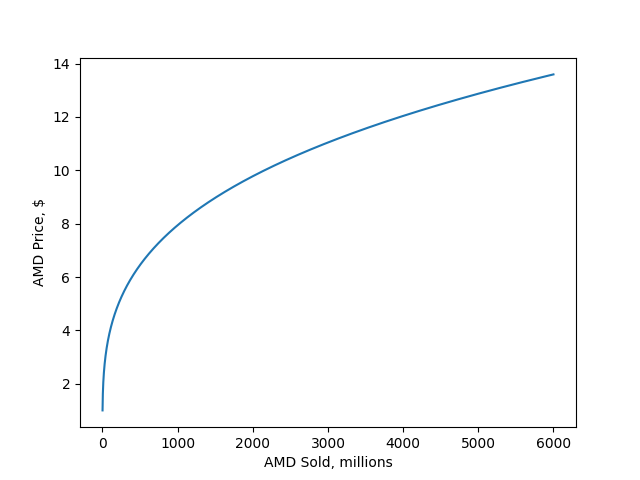
AMD Buyback Guarantee¶
The system guarantees an AMD buyback. Each AMD owner can get their invested stablecoins back minus a fee from the Ace Maker DAO:
- Within one year from the date of the transaction (AMD purchase), a return can be made with a 15% fee
- After one year, within 30 days, a return can be made with a 1.5% fee
- After one year and 30 days have passed, a return cannot be made
The buyback process closes all transactions that have not yet passed one year plus 30 days from the date of transaction. Each transaction can only be closed once and the buyback process cannot be canceled.
The AMD buyback for a single transaction is performed by the SaleAMD smart contract based on the following algorithm:
- dealAmount - the amount of AMD purchased under the transaction
- dealCost - the amount of stablecoins spent
- The system fee (buyBackFee) is calculated:
- 15% if less than one year has passed from the transaction date
- 1.5% if more than one year has passed from the transaction date but less than one year plus 30 days
- The amount to be returned (returnAmount = dealCost - buyBackFee%) is calculated
- If there are enough stablecoins in the Ace Maker DAO treasury to return the entire amount, the owner receives this amount, the transaction is closed, the owner's AMD tokens are transferred to the SaleAMD contract, locked, and can be used for resale
- If there are not enough stablecoins in the Ace Maker DAO treasury to return the entire amount:
- The missing amount is calculated
- The owner's AMD, proportional to the missing amount, is put up for sale at a Dutch auction
- If the auction raises enough funds to pay the return and system fee, the transaction is closed and the owner's AMD tokens are transferred to the auction participants
- If the auction does not raise enough funds, another auction is launched to sell copyright holders tokens from the Ace Maker DAO treasury. As soon as this auction raises enough funds to pay the return and system commission, the transaction is closed and the owner's AMD is transferred from the owner's account to the SaleAMD contract.
If the buyback process closes several transactions at once, the above algorithm is applied to each of them.
Example 1
- Alice bought 1000 AMD for 1000 stablecoins.
- Three months after the transaction, Alice initiates a buyback.
- The system fee is 15% (as it has not been a year yet).
- There are sufficient funds in the Treasury.
- 850 stablecoins are transferred from the Treasury to Alice.
- 1000 AMD is transferred from Alice to the SaleAMD contract.
Example 2
- Alice bought 3000 AMD for 3000 stablecoins.
- Three months after the transaction, Alice initiates a buyback.
- The system fee is 15% (as it has not been a year yet).
- Alice is expected to receive 2550 stablecoins (3000 - 15%).
- There are insufficient funds in the Treasury, so:
- 3000 AMD from Alice is put up for auction in the Dutch auction:
- The starting price is 1 AMD = 1.2 stablecoins.
- The price decreases by 1% every 90 seconds.
- The minimum price is 1 AMD = 0.9 stablecoins.
- Let's assume the auction raises 2800 stablecoins.
- 2550 stablecoins are transferred to Alice.
- 250 stablecoins are transferred to the Treasury (the remainder from the auction proceeds).
- 3000 AMD from Alice is transferred to the auction participants.
- 3000 AMD from Alice is put up for auction in the Dutch auction:
The Premium Asset Program for AMD Holders¶
The Premium Asset is a unique, privileged De-Fi program that provides its participants with the opportunity to receive payouts from a rewards pool generated by the Ace Maker protocol's fees and other platform revenue sources.
To participate in the Premium Asset program and receive rewards pool payouts, AMD tokens and registration are required. Registration is done by depositing AMD tokens in a special account, on terms regulated by the "Premium Asset" smart contract (tokens are staked).
This will become a key driver for acquiring, storing, and stacking AMD tokens
Holders can send their tokens to be stacked and receive rewards generated from the following sources of revenue:
-
Protocol fees from the issuance of copyright holders and content providers tokens.
30% of the total issuance amount of copyright holders tokens is credited to the Ace Maker DAO treasury at the time of issuance.
To calculate the forecasted minimum yield level from this source of revenue, use the following formula:
\[ K(S_j, S_c) = { M_r M_i \sum_{i=1}^{S_c} P(i) (F_d (1 - F_a) (1 - F_{cha} - F_{dev}) + F_p)) \over F_p S_c P(S_j)} - 1.0 \]where:
- \(K(S_j, S_c)\) - forecast of minimum AMD token yield by the end of the round \(S_c\), assuming the token was purchased on the round \(S_j\)
- \(M_r\) - the share of funds received from AMD sale used for the acquisition of tokenized broadcasting rights - 90%
- \(M_i\) - the share of investors from the total issuance of AMD tokens - 60%
- \(P(n)\) - the nominal price of the token on the round \(n\)
- \(F_d\) - system fee for issuing and managing copyright holder tokens
- \(F_a\) - agent fee (a percentage of the system fee)
- \(F_p\) - a percentage of the initial token sale
- \(F_{cha}\) - share of the protocol's revenue allocated to support charity programs - 10%
- \(F_{dev}\) - share of the protocol's revenue allocated to support technological development and marketing programs - 10%
Example calculation of the expected minimum yield for DAO members who purchased AMD tokens in the first round (the first 1 million tokens at a price of $1):
-
yield on the first round:
\[ K(1, 1) = { 0.9 * 0.6 * 1 * (0.3 * (1 - 0.1) * (1 - 0.1 - 0.1) + 0.1)) \over 0.1 * 1 * 1} - 1.0 = 70.64% \] -
yield on the second round:
\[ K(1, 2) = { 0.9 * 0.6 * 2.2311 * (0.3 * (1 - 0.1) * (1 - 0.1 - 0.1) + 0.1)) \over 0.1 * 1 * 2} - 1.0 \approx 90.36% \]
-
A 15% content provider token issuance fee, paid in stablecoins, is applied at the time of settlement between the content provider and consumer
-
The profits generated from the difference in price between the nominal and market value of copyright holders tokens purchased by the protocol
90% of the funds deposited in the Ace Maker protocol through the purchase of AMD tokens, are used exclusively to purchase 10% of issued copyright holders tokens at the nominal price. This provides AMD token holders, through the Ace Maker protocol, with exclusive and highly favorable co-ownership of broadcast and access rights to content from leading global producers such as sports organizations, movie studios, music labels, etc. This arrangement guarantees the maximum level of income from the price difference, as all future sales of copyright holders tokens will be conducted through auctions and direct sales with a minimum permissible price that exceeds the nominal, as described in the system algorithm and pricing mechanism outlined in this document.
-
By leveraging the revenue from copyright holders tokens circulation
Being a holder of AMD tokens means being a co-owner of OwnerNFT tokens, which are held in the protocol's treasury and this means participation in the distribution of income generated by the automated content distribution system, providing passive income to all OwnerNFT holders.
In addition to the payout of the price difference between the nominal and market price of content provider tokens at the time of their sale and withdrawal from the protocol, the platform also provides income in the form of a 10% fee on top of the market price, due to the complete turnover cycle of copyright holders tokens through the distribution system.
-
Other System Revenues
Stability Fee - an annual percentage calculated on top of the generated Ace Coins when collateral assets are deposited in the vault.
Liquidation Penalty - a fee added to the outstanding generated Ace Coins in case of liquidation of the collateral vault.
The specific values of the stability fee and liquidation penalty are assigned through voting by AMD token holders, separately for each type of collateral asset accepted by the system.
Distribution of the protocol’s revenue¶
20% - to Ace Maker DAO treasury special accounts for the following earmarked programs:
- 5% - for technological development and software product development
- 5% - marketing programs
- 10% - charity programs
80% - to the reward pool, for further distribution of funds among Premium Asset program participants, in proportion to the number of their tokens
Amounts allocated to the target programs and the reward pool are regulated by voting of the DAO members (AMD holders). Also, the vote will determine what portion of the funds will be automatically reinvested in the protocol and what will be paid out to AMD holders as reward.
Ace Stable Coin (Ace Coin)¶
The primary objective of creating the "Ace Stable Coin" is to establish a multi-currency mechanism for facilitating cross-border payments and conducting convenient automated settlements in the multimedia market. This will provide seamless global access to premium content from leading global producers using DLT and P2P broadcasting technologies, empowering all market participants and decentralized network users to expand their rights and opportunities.
Ace Coin is a decentralized stable digital currency with a soft peg to various national currencies, backed by high-liquidity digital assets. The maximum decentralization and the most valuable assets of the internet network, such as broadcast rights and access to premium content, as well as internet network bandwidth capabilities, form the foundation and collateral for Ace Coin.
Ace Coin Collateral Assets¶
The creation, support and maintenance of the stability of Ace Coins is facilitated by the tokenized assets deposited into the Ace Maker protocol vaults as base, reserve, and collateral assets.
Approved collateral assets as of the publication of this document:
-
Base Collateral
- Copyright holders tokens
The base collateral serves as the foundation for the creation of Ace Coins.
Only tokens held by leading global content creators with a proven track record and a high level of reputation can serve as base collateral.
-
Reserve collateral
- USD Coin USDC
- Dai DAI
- Tether USDT
The reserve collateral serves as the foundation for the creation of Ace Coins and helps maintain its liquidity.
Only stable digital financial assets with a guaranteed monetary backing, such as stablecoins, bank-issued or bank-guaranteed certificates of deposit, high-rated issuer bonds, etc. can serve as reserve collateral.
-
Volatile collateral
- Bitcoin wBTC
- Ethereum ETH
Volatile collateral serves as the foundation for the creation of Ace Coins through the lending mechanism.
Only stable financial assets and reliable digital currencies with high volatility levels, as well as highly liquid digital assets backed by goods and services can serve as volatile collateral.
The collateral assets are digital assets that Ace Maker DAO token holders have agreed to accept when working with the Ace Maker protocol. Holders of AMD tokens agree on specific risk parameters for each digital asset accepted as collateral. These and other decisions are made within the framework of the decentralized Ace Maker management process.
The liquidity of Ace Coin is ensured by the Ace Maker protocol, with its base and reserve collateral fully covering liquidity risks. All the circulating Ace Coin currency has an excessive backing. This means that the value of the collateral exceeds the amount of Ace Maker DAO debt obligations. All Ace Coin transactions are publicly accessible on the Ethereum blockchain.
Properties and Use Cases of Ace Coin¶
Ace Coin is the exclusive currency in the Ace Maker protocol, used for paying system fees and settling transactions with content providers and other protocol users. Additionally, Ace Coin can be used to pay for traffic (CDN) and access to all services and products within the Ace Stream network, which boasts over 30 million users.
Ace Coin serves as a medium of exchange while retaining its worth, offering a convenient and efficient alternative to traditional currencies
Ace Coin as a Savings Asset
A savings asset is a type of investment that retains its value over time. With access to popular sporting events (such as football, boxing, basketball, etc.) and content produced by the world's leading film studios, Ace Coin holders can be confident that even if fiat currencies depreciate, a currency backed by such an asset will not lose its value. The enjoyment of watching competitions and other spectacles has been in high demand even before the existence of fiat currencies and will continue to have value after them.
Ace Coin is a stablecoin, making it a suitable option for savings even in volatile market conditions. Unlike traditional fiat money and centralized stablecoins, one of the key advantages of Ace Coin is that the funds cannot be blocked or taken away by third parties without the owner's consent or direct involvement.
Ace Coin as a Medium of Exchange
A medium of exchange is an asset that serves as a standard of value and acts as an intermediary in the sale, purchase, or exchange of goods and services.
Ace Coin can be used worldwide for conducting any type of commercial transactions with a soft peg to the currency of any country.
Ace Coin as a Measure of Value
Value is a standard unit of measure that represents the worth of goods and services, for example, the US dollar, euro, or yen.
Ace Coin uses a multi-currency mechanism and its target value is pegged to the currency of the country to which it was linked at the time of its issuance (as described in detail in the TokenizedCopyrightsManager smart contract). Currently, the target value of Ace USD is equal to 1 US dollar (1 AceUSD = 1 USD), and Ace EUR is equal to 1 euro (1 AceEUR = 1 EUR). Outside of the blockchain, Ace Coin is not used as a standard measure of value, but it performs this function within the Ace Maker protocol and in some decentralized blockchain applications. Thus, calculations in the Ace Maker protocol or pricing in decentralized applications are made in Ace Coin, rather than in a government currency like the US dollar or euro.
Ace Coin as a Liquidity Unlocker and Investment Generator
Anyone can create the required amount of Ace Coins by providing guarantees for their return, in order to obtain affordable investment resources by utilizing unused or previously disregarded assets. In addition, the issuer is also given the opportunity to multiply the created and received Ace Coins through the exclusive "Premium Asset" program.
This is yet another advantage of Ace Coin over other stablecoins.
Ace Coin as a means of deferred payment
Ace Coin is used for settling debts within the Ace Maker protocol (for example, vault debts are paid in Ace Coins, as well as copyright holders tokens are also purchased by protocol with Ace Coins).
The issuance of Ace Coin¶
The issuance of Ace Coin is automated through the Ace Maker protocol, triggered by the following events:
- Adding copyright holders tokens to the protocol through the TokenizedCopyrightsManager smart contract
- Adding reserve assets to the protocol through the Peg Stability Module
- Depositing crypto assets into the Ace Maker vault as collateral for lending purposes
Ace Coins created through these events are pegged to the currency specified by the issuer and are designated with a currency code (e.g. Ace USD, Ace EUR, etc.). The list of acceptable currency pegs is determined by AMD token holders
Ace Maker Vaults¶
All approved assets in the Ace Maker protocol can be used as collateral to create Ace Coins through smart contracts known as Maker Vaults. There are three types of Maker Vaults in the Ace Maker protocol:
- Vault for base assets - for storing tokenized copyrights (copyright holders tokens)
- Peg Stability Module (PSM) - for storing reserve assets
- Vault for volatile assets - for storing volatile collateral
Vault for Base Assets¶
For each copyright holder in the Ace Maker protocol, a separate vault is created. The purpose of this vault is to store copyright holder tokens as a collateral. Only the TokenizedCopyrightsManager smart contract can create this type of vault and deposit base assets. This contract encapsulates the tokenization of accepted assets and provides authorization (by requesting digital signatures from decentralized entities whose permission is required to deposit assets).
Only AMD token holders can deposit base assets into the protocol through voting. As a result of depositing the asset, the protocol generates an Ace Coin in an amount corresponding to the estimated value of the asset.
Risky Vault Liquidation for Base Assets
For each type of base asset, a liquidity coefficient is assigned. AMD token holders determine it by voting based on the risk profile of a particular type of base asset. The protocol tracks the riskiness of the vault by comparing the liquidity coefficient with the current ratio of asset value to debt in the vault. If this ratio falls below the liquidity coefficient, the vault is considered risky, and the system launches an auction to sell part of the asset and repay the debt.
Vault for Reserve Assets¶
The Peg Stability Module (PSM) is a special type of vault that accepts stablecoins as collateral. PSM facilitates the exchange of Ace Coins and stablecoins at a 1:1 ratio. Any account in the network can deposit stablecoins into PSM and receive Ace Coins in exchange, or vice versa. The list of stablecoins accepted by PSM is approved by AMD holders.
For example, depositing 1000 USDC results in the account receiving 1000 Ace USD.
Vault for Volatile Assets¶
These vaults are inherently non-custodial: Users interact with Vaults and the Ace Maker Protocol directly, and each user has complete and independent control over their deposited collateral as long the value of that collateral doesn’t fall below the required minimum level (the Liquidation Ratio, discussed in detail below).
Interacting with a Vault¶
Creating a Vault is not complicated, but generating Ace Coin does create an obligation to repay the Ace Coin, along with a Stability Fee, in order to withdraw the collateral leveraged and locked inside a Vault.
Step 1: Create and Collateralize a Vault
A user creates a Vault via the Eden portal or a community-created interface by funding it with a specific type and amount of collateral that will be used to generate Ace Coin. Once funded, a Vault is considered collateralized.
Step 2: Generate Ace Coin from the Collateralized Vault
The Vault owner initiates a transaction, and then confirms it in their unhosted cryptocurrency wallet in order to generate a specific amount of Ace Coin in exchange for keeping their collateral locked in the Vault.
Step 3: Pay Down the Debt and the Stability Fee
To retrieve a portion or all of the collateral, a Vault owner must pay down or completely pay back the Ace Coin they generated, plus the Stability Fee that continuously accrues on the Ace Coin outstanding. The Stability Fee can only be paid in Ace Coin.
Step 4: Withdraw Collateral
With the Ace Coin returned and the Stability Fee paid, the Vault owner can withdraw all or some of their collateral back to their wallet. Once all Ace Coin is completely returned and all collateral is retrieved, the Vault remains empty until the owner chooses to make another deposit.
Importantly, each collateral asset deposited requires its own Vault. So, some users will own multiple Vaults with different types of collateral and levels of collateralization.
Liquidation of Risky Volatile Asset Vaults¶
To ensure there is always enough collateral in the Ace Maker Protocol to cover the value of all outstanding debt (the amount of Ace Coin outstanding valued at the Target Price), any collateralized vault deemed too risky (according to parameters established by Ace Maker Governance) is liquidated through automated Ace Maker Protocol auctions. The Protocol makes the determination after comparing the Liquidation Ratio to the current collateral-to-debt ratio of a vault. Each vault type has its own Liquidation Ratio, and each ratio is determined by AMD voters based on the risk profile of the particular collateral asset type.
Ace Maker Liquidation Auctions for Risky Vaults¶
The auction mechanism in the Ace Maker Protocol enables the system to liquidate collateral vaults for base and volatile assets deemed too risky. During the liquidation process, collateral is either fully or partially withdrawn from the vault and sold through the internal auction mechanism. This auction is referred to as the Liquidity Auction and is conducted using the Dutch auction system, which ensures the quickest closure time.
The Ace Coins obtained from the Liquidity Auction are directed towards covering the outstanding debt of the vault. In the case of liquidation of a vault with volatile assets, the auction proceeds must also cover the liquidation penalty established by the AMD token holders voting for that specific type of collateral in the vault.
If the Liquidity Auction fails to attract sufficient Ace Coins to cover the vault's outstanding debt, the deficit becomes the debt of the protocol.
The System Stabilization Module¶
The System Stabilization Module is designed to correct the system in the event that the value of the assets deposited into the protocol falls below a level determined by the AMD token holders. In this case, a protocol debt arises, which is eliminated by the following mechanisms:
- The protocol debt is repaid using Ace Coin from the Ace Maker treasury.
- If there is not enough Ace Coin in the treasury to repay the debt, auctions are launched to sell assets (such as copyright holders tokens) from the Ace Maker treasury. The resulting Ace Coin is used to repay the debt.
- If the debt cannot be repaid through auctions within the set time frame, and all AMD tokens from the SaleAMD contract have been sold, a debt auction is launched. During the debt auction, AMD tokens are emitted (thus increasing their circulation), which are then sold for Ace Coin.
Emergency Shutdown¶
Emergency Shutdown (or, simply, Shutdown) serves two main purposes. First, it is used during emergencies as a last-resort mechanism to protect the Ace Maker Protocol against attacks on its infrastructure. Emergencies could include malicious governance actions, hacking, security breaches, and long-term market irrationality. Second, shutdown is used to facilitate an Ace Maker Protocol system upgrade. The shutdown process can only be controlled by Maker Governance.
AMD voters are also able to instantly trigger an Emergency Shutdown by depositing AMD into the Emergency Shutdown Module (ESM), if enough AMD voters believe it is necessary. This prevents the Governance Security Module (if active) from delaying Shutdown proposals before they are executed. With Emergency Shutdown, the moment a quorum is reached, the Shutdown takes effect with no delay.
There are four phases of Emergency Shutdown:
-
The Ace Maker Protocol shuts down; vault owners withdraw assets.
When initiated, Shutdown prevents further vault creation (both with base and volatile assets) and manipulation of existing vaults, and freezes the Price Feeds. The frozen feeds ensure that all users are able to withdraw the net value of assets to which they are entitled. Effectively, it allows owners of vaults with volatile assets to immediately withdraw the collateral in their vault that is not actively backing debt.
-
Post-Emergency Shutdown auction processing
After Shutdown is triggered, Liquidation Auctions for vaults with volatile assets begin and must be completed within a specific amount of time. That time period is determined by Ace Maker Governance to be slightly longer than the duration of the longest Liquidation Auction. This guarantees that no auctions are outstanding at the end of the auction processing period.
-
Ace Coin holders claim remaining collateral
At the end of the auction processing period, Ace Coin holders use their Ace Coin to claim collateral directly at a fixed rate that corresponds to the calculated value of their assets based on the Ace Coin target price. There is no time limit for when a final claim can be made. Ace Coin holders will get a proportional claim to each collateral type that exists in the collateral portfolio.
-
Treasury funds and base assets are transferred to reserve accounts, which are determined by AMD voters.
The Future of Ace Maker Protocol¶
System Optimization¶
Ace Maker DAO plans to utilize ZK Rollup technology to optimize the system, reducing transaction time and lowering transaction fees.
Decentralized Exchange (DEX)¶
The creation of a specialized decentralized exchange, focused on working with assets issued within the Maker DAO protocol.
Cross-Margin Trading on DEXs¶
The implementation of a cross-chain protocol for margin trading on decentralized exchanges.
This will allow traders to trade on DEXs with leverage and holders of Ace Coins to receive high staking interest rates (up to 12% annually on deposit).